Castanea and Hamamelis
biogeography
Hamamelis (the witch-hazels) and Castanea (chestnuts) are two classic examples exhibiting the well-known eastern Asian (EA)-eastern North American (ENA) disjunct distribution. Our results showed congruences in phylogenetic inference and divergence time dating between RAD-seq and Hyb-Seq data sets.


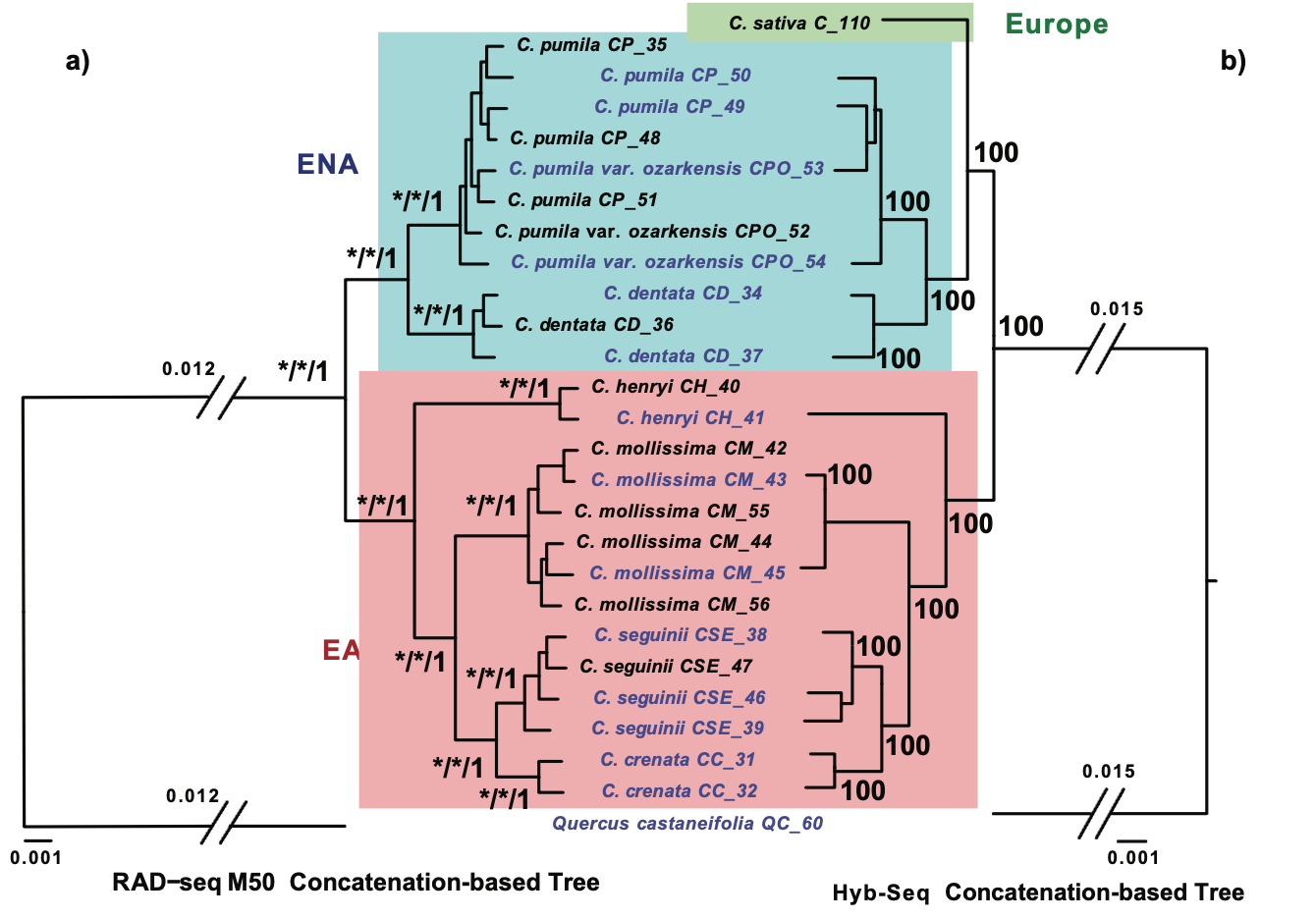
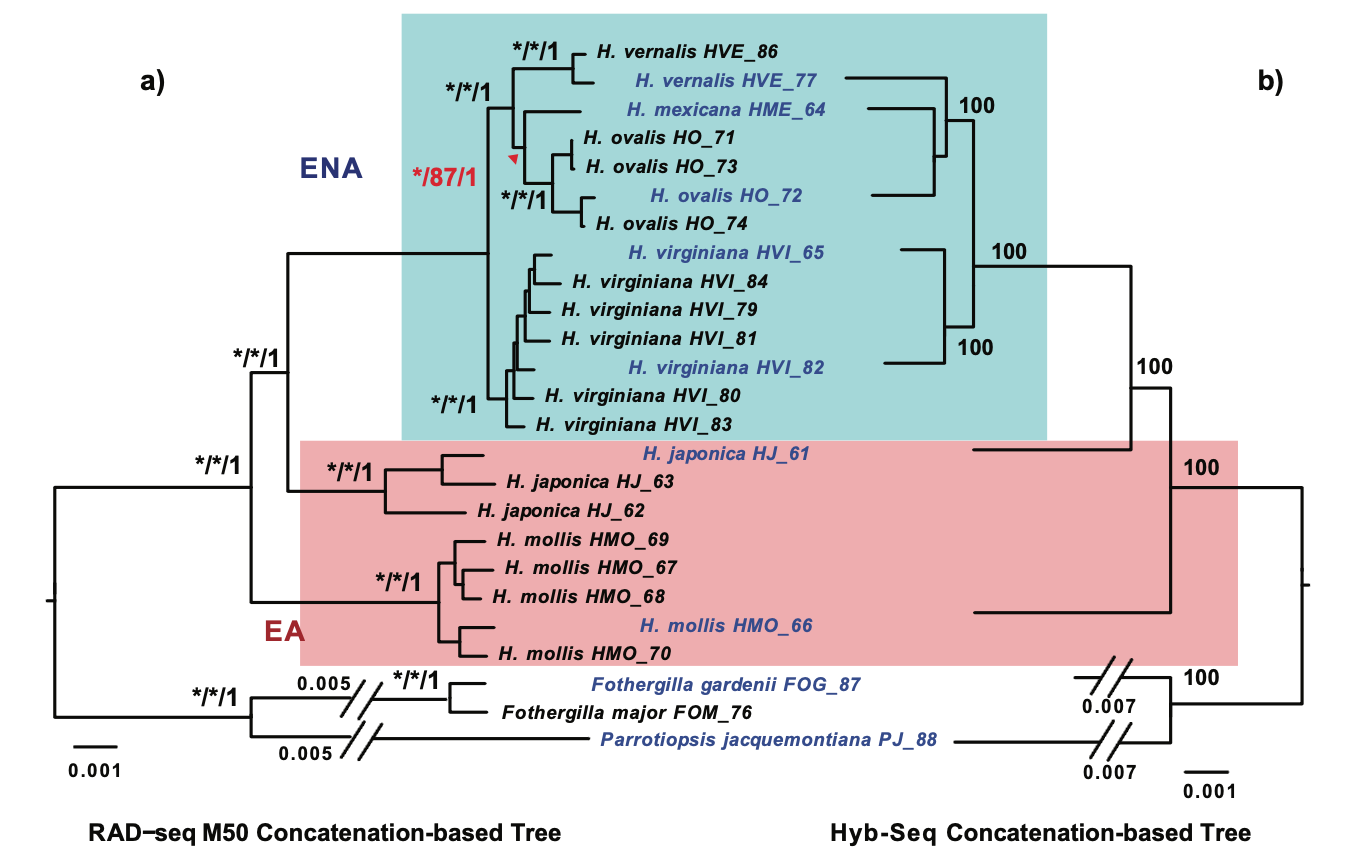
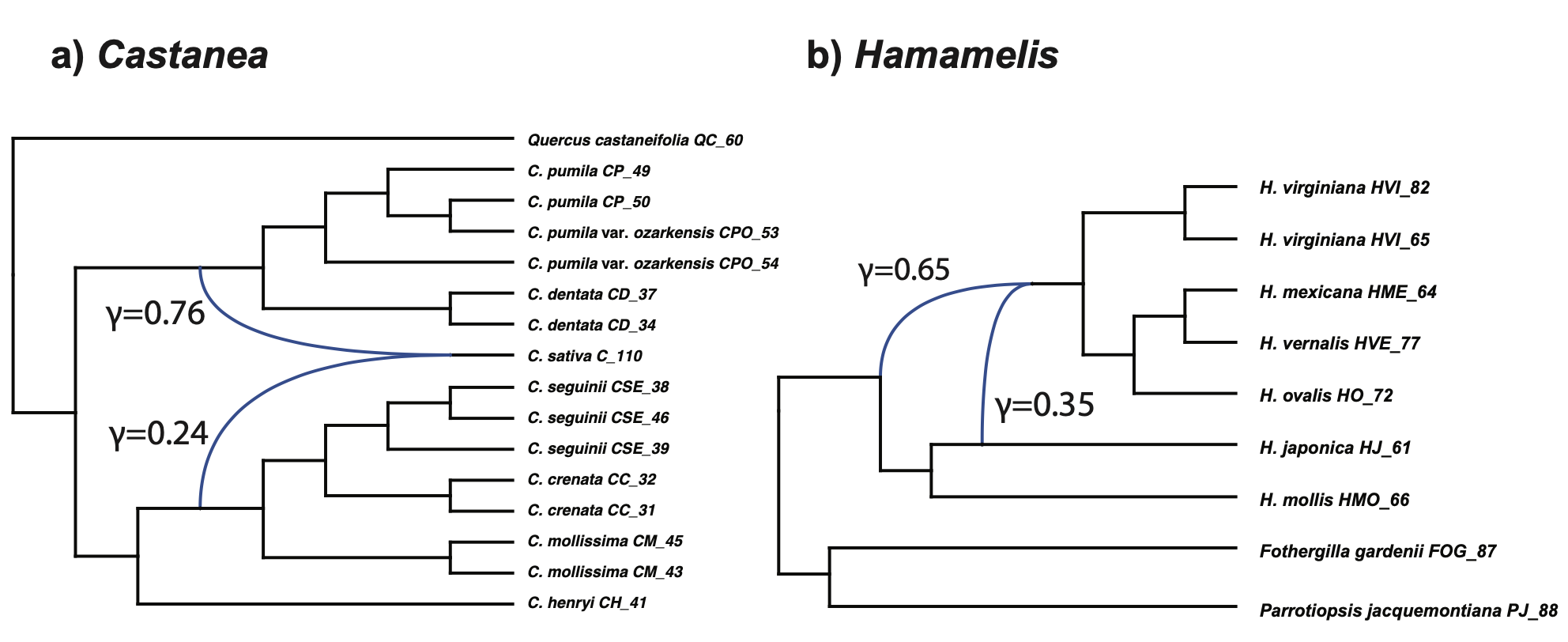
Our phylogenetic analyses of RAD-seq and Hyb-Seq data resulted in well-resolved species relationships. Analyses of the data using the D-statistic test and PhyloNet revealed ancient introgressions in both genera. Biogeographic analyses including fossil data using total evidence-based dated tree and DEC model applying specific inter-area dispersal probabilities revealed a complicated history for each genus, indicating multiple interareal dispersals and local extinctions within and outside areas of the taxa’s modern ranges in both the Paleogene and Neogene.
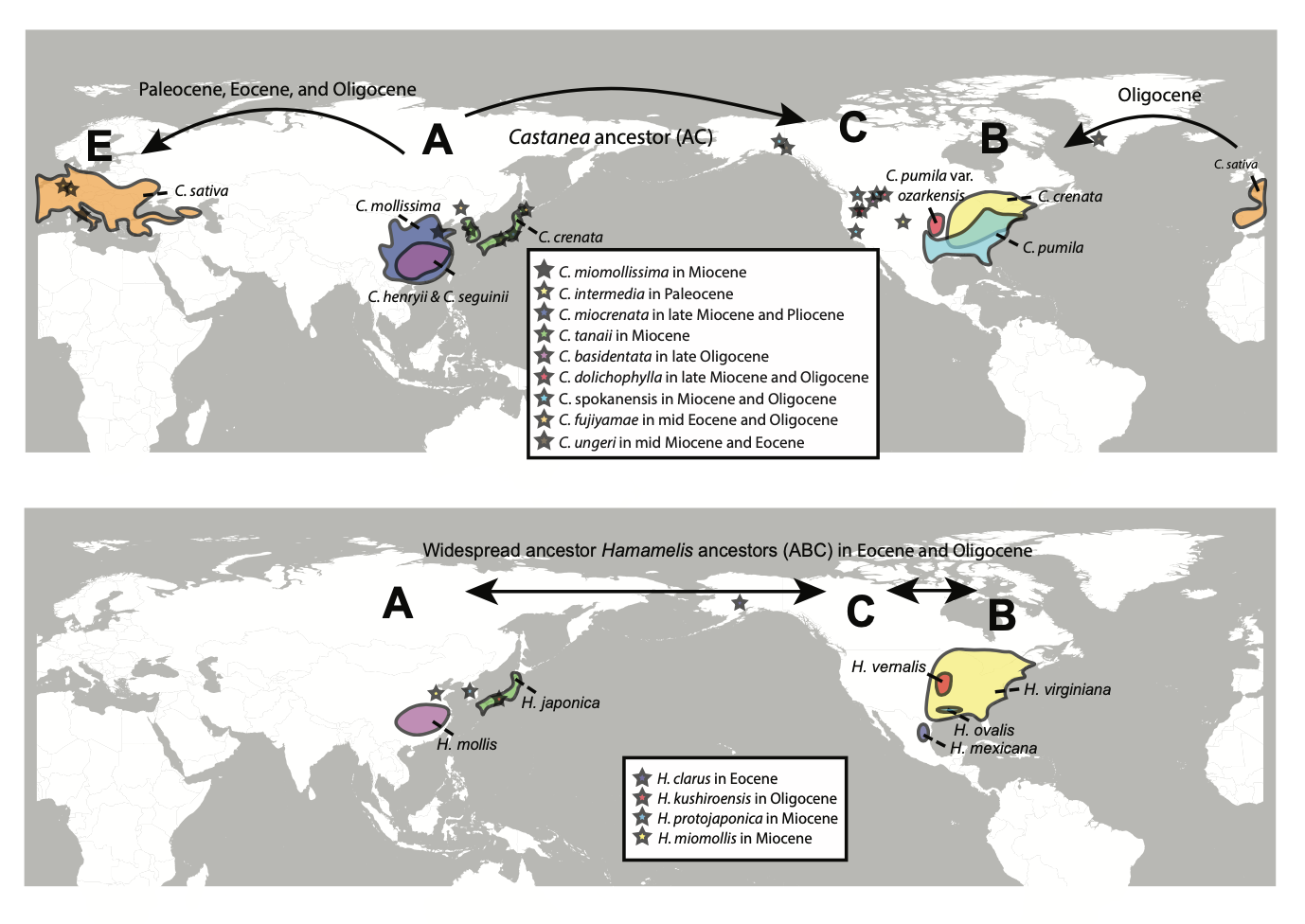
The study demonstrates the importance of including fossil taxa for a more accurate reconstruction of biogeographic histories of taxa to understand the EA and ENA floristic disjunction. Our results support a widespread ancestral range in EA-western North America (WNA) followed by early diversification in EA and expansion to North America (NA) and Europe for Castanea and a more widespread ancestral range in EA-ENA-WNA for Hamamelis. The origins of the modern EA-ENA disjunction in both genera were suggested to be the result of vicariance from widespread ancestors in Eurasia-ENA of the mid-Miocene and in EA-NA of the late Oligocene, respectively.
This paper is under review in MPE (accepted with major issue).